Removing an adhd diagnosis: insight into the process and causes
A growing trend among individuals diagnosed with ADHD is the desire to have their diagnoses reconsidered or removed. This desire is often driven by factors such as a change in self-perception or the diagnosis being perceived as an obstacle in professional life and education.
Why do you want to remove the diagnosis?
A growing proportion of people living with a diagnosis find that they outgrow their ADHD symptoms in adulthood. In addition, an ADHD diagnosis can be perceived as a barrier in various aspects of life, such as when applying for certain courses or professions, which may warrant a reconsideration of the diagnosis.
The process of removing the diagnosis
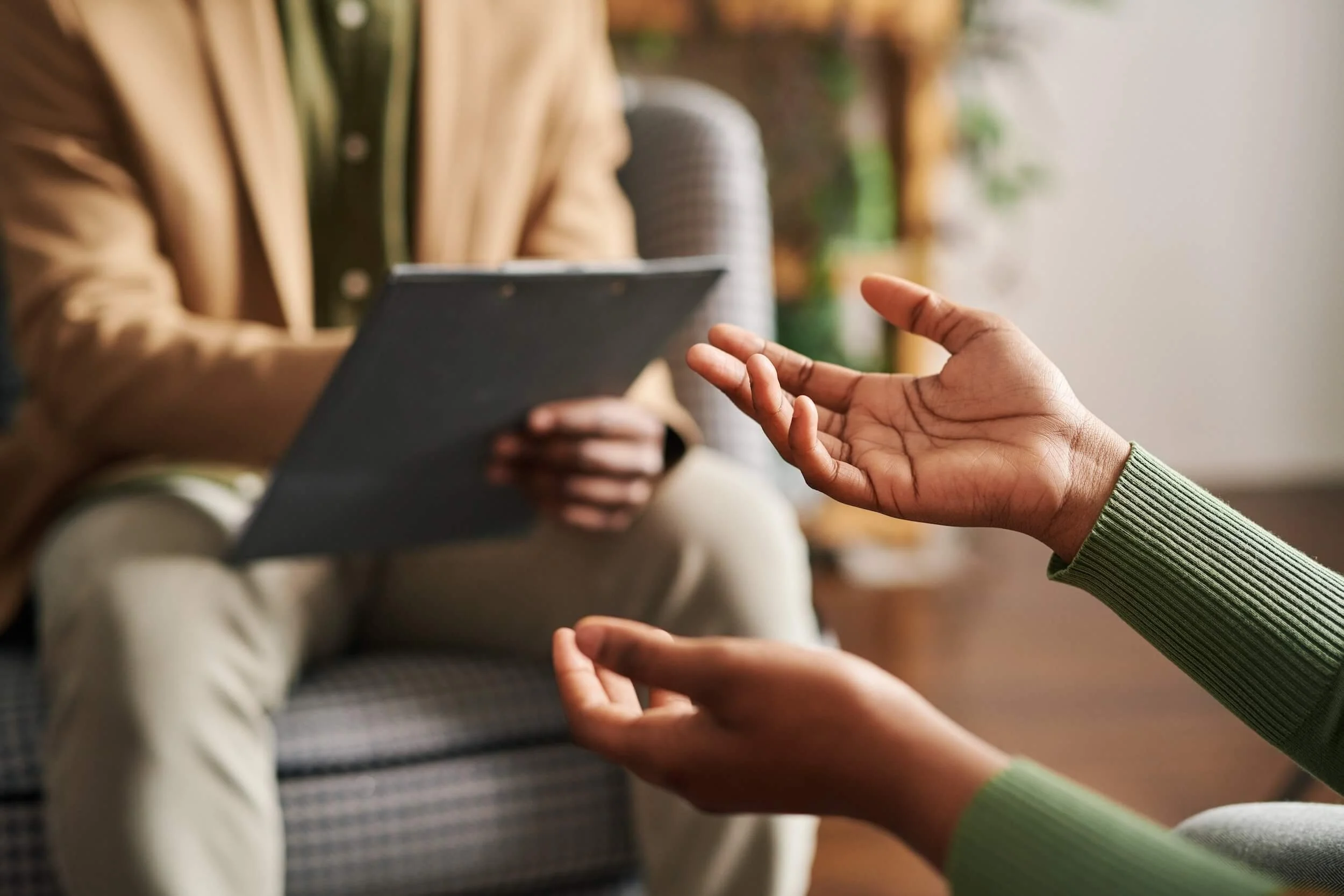
To reconsider a diagnosis of ADHD, individuals can turn to private healthcare providers. The process involves filling out forms that assess the individual's current mood and functioning. It is common to have to wait at least two years after the diagnosis was made before it can be reviewed. At Sveapsykologerna, we offer specialized counseling and ADHD assessments to create tailored plans for each person.
Reconsideration of a diagnosis
Reassessment of an ADHD diagnosis involves a thorough evaluation of the individual's current symptoms and how these affect their daily life. It may involve psychological tests and a review of the individual's medical history, as well as a new neuropsychiatric assessment. The aim is to ensure that the diagnosis is still relevant and accurate. This step is crucial to understand how the diagnosis affects the individual's life and whether it is still applicable.
Help with removing the diagnoses ADD, Autism and functional impairment
Sveapsykologerna has an experienced team that can help you get rid of or write off diagnoses you have received in ADD, autism and also functional impairment.
Psychologists in Stockholm, Gothenburg and Malmö to help you
Sveapsykologerna offers help with dismissing or reconsidering ADHD diagnoses in Stockholm, Gothenburg, Malmö and also online. Contact our experienced psychologists and doctors to book a free consultation about your questions.
Challenges and perspectives of removing a diagnosis
Despite the growing interest in de-diagnosing ADHD, there are challenges, such as limited healthcare resources and disagreements about the responsibilities of healthcare units in the de-diagnosis process.
We at Sveapsykologerna are involved in meeting these challenges by developing standardized investigation processes to write off diagnoses.
Frequently asked questions about removing an ADHD diagnosis
-
Yes, an ADHD diagnosis can be reconsidered and possibly removed if it is no longer considered to meet diagnostic criteria.
-
The first steps involve contacting a healthcare provider for an initial assessment, and then undergoing a new neuropsychiatric assessment.
-
The length of the process varies depending on the individual's situation. We make an individual assessment for each unique case and cannot give exact times as many factors come into play. We start the investigation immediately to help you get started.
-
Factors such as the individual's current symptoms, impact on daily life, past medical history and life changes are considered.
-
Yes, reassessment of ADHD diagnoses may occur even if still on medication, but this will be taken into account in the evaluation.
-
A previous diagnosis is not an obstacle to reconsideration, but the medical history will be taken into account in the assessment.
-
Qualified professionals such as psychologists and psychiatrists may reconsider the diagnosis.
-
Self-assessment is important to understand the individual's experience, but professional assessment and tests are crucial for the final decision.
-
A reassessed diagnosis may affect access to certain supports and resources, which should be considered in the decision-making process.
-
The process may differ between children and adults, especially in terms of assessment content and methodology.
-
Family opinions and observations can be valuable, especially when assessing children, but the decision is primarily based on professional judgment.
-
There is a risk that the individual's need for support and adaptations may be overlooked if the diagnosis is reconsidered without justification.
-
Confidentiality and integrity are strictly maintained throughout the process in accordance with applicable laws and ethical guidelines.
-
If the diagnosis is confirmed, support and treatment plans continue as before, and additional resources or adaptations may be considered.